Dominion Atlantic Railway Digital Preservation Initiative - Wiki
Use of this site is subject to our Terms & Conditions.
Category:Windsor and Annapolis Railway
Windsor and Annapolis Railway Company, Limited

See also: the 1867 W&AR Prospectus
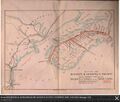
The Windsor and Annapolis Railway (W&AR) was the most significant of the founding companies of the Dominion Atlantic Railway. The W&AR was formed by Nova Scotian railway promoters and British investors in 1864 to connect the government owned "Windsor Branch" of the Nova Scotia Railway at Windsor with Annapolis Royal. Investors were attracted by the traffic potential between Halifax, Bay of Fundy and New England ports as well as the apple orchards of the Annapolis Valley.[1] Construction was completed in 1869. The railway struggled at first but soon developed a growing passenger and freight traffic from the Annapolis Valley. Built at first to the broad gauge of 5' 6", it converted to standard gauge of 4' 8½" in 1875. The W&AR faced a formidable rival in the Western Counties Railway (WCR) which used political connections several times to take control of the lucrative "Windsor Branch". The W&AR merged with the WCR in 1894 to create the Dominion Atlantic Railway with the W&AR's old mainline becoming the Halifax and Middleton subdivisions of the Dominion Atlantic. The W&AR was the senior partner in the merger which established the old W&AR headquarters in Kentville as the headquarters of the new company. The Dominion Atlantic inherited the W&AR's "Land of Evangeline" identity and the W&AR's livery of bright magenta red locomotives. The W&AR was also a small-scale builder of wooden railway passenger and freight cars at its Kentville Shops, building several cars that survived into the DAR fleet.
W. & A. R. had a special rail customer during the 1880's—The Palace RR Photograph Car Company. They operated a special photo car which was a mobile photograph studio which would travel the line. A Lewis Rice operated one of these such cars along with his photographic studios in Windsor & Wolfville.[2]
Car Builder
The W&AR built a series of passenger cars as few as a few freight cars at their Kentville Car Shop. Several passenger cars were built in the winter months of 1887 and 1888[3]. during the time that W. Grierson served as master car builder.[4]
Cars built by the W&AR included:
Coach No. 4
Coach No. 5
Coach No. 6
Baggage No. 52
Baggage No. 53
Baggage No. 55
Baggage No. 56
W&AR Locomotives
These are the W&A broad gauge locomotives, 9 of which were traded to the Canadian Government on July 1, 1875, that never made it to the DAR roster.
- W&AR Joseph Howe, - second hand from Canadian Government
- W&AR Sir Gaspard le Marchant, - second hand from Canadian Government
- W&AR St. Lawrence, - Portland
- W&AR No. 1 First "Evangeline", - Messrs. Fox, Walker & Co., traded to the ICR 1875
- W&AR No. 2 First "Gabriel", - Messrs. Fox, Walker & Co., , traded to the ICR 1875
- W&AR No. 3 First Hiawatha, - Messrs. Fox, Walker & Co., traded to the ICR 1875
- W&AR No. 4 First Blomidon/Minnehaha, - Messrs. Fox, Walker & Co., traded to the ICR 1875
- W&AR First Gaspereau, - Messrs. Fox, Walker & Co.
- W&AR First Grand Pre, (destroyed January 5, 1872 by fire at the Halifax Roundhouse) - Messrs. Fox, Walker & Co.
- W&AR First Mic-Mac
- W&AR Maliseet
- W&AR First Minnehaha
- W&AR St. Croix - second hand from Portland in 1871
- W&AR Lightning - second hand from Great Western Railway in 1871
The locomotives below are the W&A standard gauge locomotives which later became DAR locomotives.
- W&AR No. 1 Second "Evangeline" later DAR No. 14
- W&AR No. 2 Second "Gabriel" later DAR No. 13
- W&AR No. 3 Second "Hiawatha" later DAR No. 2
- W&AR No. 4 "Blomidon" possibly later DAR No. 4
- W&AR No. 6 later DAR No. 3
- W&AR No. 8 "Benedict" later DAR No. 5
- W&AR No. 9 Second "Minnehaha" later DAR No. 6
- W&AR No. 10 "Kentville" later DAR No. 12
- W&AR No. 11 "St. Eulalie" later DAR No. 9
- W&AR No. 12 "Acadia" later DAR No. 11
- W&AR No. 13 "Queen Mab" later DAR No. 1
- W&AR No. 14 "Atlanta" later DAR No. 16
- W&AR No. 15 "Oberon" later DAR No. 19
- W&AR No. 16 "" later DAR No. 20
W&AR Rolling Stock
See:
W&AR Passenger Cars
W&AR Box Cars
W&AR Flat Cars
W&AR Gondolas
W&AR Stock Cars
Gallery
Colour drawing and cross section by the Fox Walker Company of the Windsor & Annapolis locomotive No. 1 "Evangeline", 1868.
Detail of title and steam dome from colour drawing by the Fox Walker Company of the Windsor & Annapolis Railway locomotive No. 1 "Evangeline", 1868.
Detail of the wheel splasher with engine name from colour drawing by the Fox Walker Company of the Windsor & Annapolis Railway locomotive No. 1 "Evangeline", 1868.
Detail of cab side with builders plate from colour drawing by the Fox Walker Company of the Windsor & Annapolis Railway locomotive No. 1 "Evangeline", 1868.
The first recorded photo of the Kentville Station taken in August 1869, also showing the Freight Shed and Car Shop.
Windsor and Annapolis marks one year of operation. See also the article text here.
Lighting, a broad gauge locomotive in front of the W&AR Kentville Engine House and Machine Shop in 1872.
Lighting, a broad gauge locomotive in front of the W&AR Kentville Engine House and Machine Shop in 1872.
Windsor and Atlantic Railway letterhead by General Manager Vernon Smith 1869-1872, thought to represent the line at Mill Brook near Kentville from the Comeau Family Collection.
The first Annapolis Royal Station station, circa 1880.
Annapolis Royal Railway Wharf with Windsor and Annapolis Railway train meeting the paddlewheeler Empress with a W&AR monitor-top baggage car & W&AR flat car and insulated box car, circa 1880.
W&A locomotive No. 2 "Gabriel" at the Annapolis Royal Station, decorated for the wedding of W&AR manager John W. King, June 1885.
2nd Generation Windsor & Annapolis Railway Station plans, circa 1880, based on the the Lawrencetown Station, drawn by Dan Conlin, 2004.
Berwick Station during the apple export season with a W&AR box car, circa 1890.
Excavation at Kentville with Windsor and Annapolis Railway flat car No. 84, probably leveling of the hill which became the Cornwallis Inn, circa 1890.
Windsor & Annapolis No. 15 "Oberon" builder's (Baldwin) photo in 1893. This locomotive became the DAR No. 19.
W&A No. 16 "Titania" that become DAR No. 20 "Titania".
Windsor & Annapolis Railway engraving of the Annapolis Royal Wharf, 1893.
References and Footnotes
- Gary Ness's Canadian Pacific's Dominion Atlantic Railway (Vol. I), page 1, (Vol. II), page 13.
- Marguerite Woodworth, History of the Dominion Atlantic Railway, pages 51-87.
- ↑ Prospectus, WINDSOR AND ANNAPOLIS RAILWAY NOVA SCOTIA, London: J. Haddon & Co. Printers (1867), Copy No. 24 Comeau Family Collection, p. 3-4, p. 5-6
- ↑ Tom Sheppard, Historic Wolfville: Grand Pre and Countryside, page 178.
- ↑ Andrew Merrilees, "Railway Rolling Stock Industry in Canada", Library and Archives Canada MG31 A10 Vol. 54
- ↑ Annapolis Spectator, June 13, 1890
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.
W
Pages in category "Windsor and Annapolis Railway"
The following 43 pages are in this category, out of 43 total.
D
W
- W&AR
- W&AR 1867 Prospectus
- W&AR Box Cars
- W&AR Flat Cars
- W&AR Gondolas
- W&AR Passenger Cars
- W&AR Stock Cars
- W&AREVANGELINE
- W&ARGABRIEL
- W&ARLightning
- W&ARMINNEHAHA
- Windsor & Annapolis
- Windsor & Annapolis Railway
- Windsor and Annapolis
- Windsor and Annapolis Railway
- Windsor and Annapolis Railway, Report of Alexander MacNab 1873
- Windsor and Atlantic Railway